Viewing IFC using ModelConverter and XGFLoader
Use the ModelConverter class to convert a model from IFC format into XGF, then use XGFLoader to load the XGF into a xeokit web viewer.
Click on the preview below to run the example. Scroll down to learn how it's made.
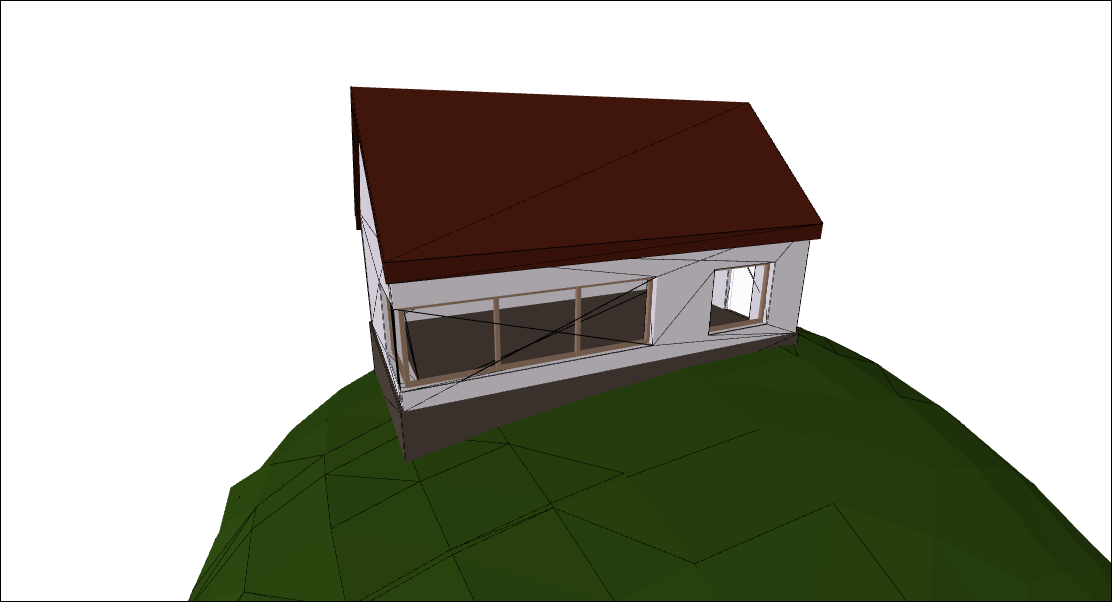
Viewing IFC using ModelConverter and XGFLoader
HTML
Listed below is the HTML for this example.
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Viewing IFC using ModelConverter and XGFLoader</title>
<style>
body {
background-color: white;
overflow: hidden;
margin: 0;
user-select: none;
}
#demoCanvas {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
position: absolute;
background: white;
border: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="demoCanvas"></canvas>
</body>
<script type="module" src="./index.js"></script>
</html>
JavaScript
Listed below is the JavaScript for this example, which we'll break down into steps.
1. Import the xeokit SDK bundle built specifically for the example environment
import * as xeokit from "../../js/xeokit-demo-bundle.js";
import {DemoHelper} from "../../js/DemoHelper.js";
2. Create a ModelConverter
@xeokit/sdk / modelconverter / ModelConverter / Class ModelConverter Transforms 3D model data between different file formats. @xeokit/sdk / data / DataModelParams / Interface DataModelParams Parameters used to define a DataModel. @xeokit/sdk / ifc / IFCLoader / Class IFCLoader Loads an IFC file into a SceneModel
@xeokit/sdk / scene / SceneModel / Class SceneModel Contains a model's geometry and materials. @xeokit/sdk / xgf / XGFExporter / Class XGFExporter Exports a SceneModel to an XGF file. @xeokit/sdk / data / DataModelParamsExporter / Class DataModelParamsExporter Writes a DataModel to DataModelParams as JSON.
const modelConverter = new xeokit.modelconverter.ModelConverter({
loaders: {
"ifc": new xeokit.ifc.IFCLoader()
},
exporters: {
"xgf": new xeokit.xgf.XGFExporter(),
"datamodel": new xeokit.data.DataModelParamsExporter()
},
pipelines: {
"ifc2xgf": {
inputs: {
"ifc": {
loader: "ifc",
options: {}
}
},
outputs: {
"xgf": {
exporter: "xgf",
version: "1.0",
options: {}
},
"datamodel": {
exporter: "datamodel",
version: "1.0",
options: {}
}
}
}
}
});
3. Create a Scene
@xeokit/sdk / scene / Scene / Class Scene Container of model geometry and materials.
const scene = new xeokit.scene.Scene();
4. Create a Data
@xeokit/sdk / data / Data / Class Data Container of model semantic data.
const data = new xeokit.data.Data();
5. Initialize a WebGLRenderer
@xeokit/sdk / webglrenderer / WebGLRenderer / Class WebGLRenderer WebGL rendering strategy for a Viewer.
const renderer = new xeokit.webglrenderer.WebGLRenderer({});
6. Create a Viewer
@xeokit/sdk / viewer / Viewer / Class Viewer 3D model viewer.
const viewer = new xeokit.viewer.Viewer({
id: "demoViewer",
scene,
renderer
});
7. Create a single View
@xeokit/sdk / viewer / View / Class View An independent view within a Viewer, with its own canvas, Camera and object visual states.
const view = viewer.createView({
id: "demoView",
elementId: "demoCanvas"
});
8. Arrange the View's Camera
@xeokit/sdk / viewer / Camera / Class Camera Controls the viewpoint and projection for a View.
view.camera.eye = [-6.01, 4.85, 9.11];
view.camera.look = [3.93, -2.65, -12.51];
view.camera.up = [0.12, 0.95, -0.27];
9. Add interactive controls for navigating the View using mouse, keyboard, and touch
new xeokit.cameracontrol.CameraControl(view, {});
10. Create a SceneModel to store the geometry and material data for the model
const sceneModel = scene.createModel({
id: "demoModel"
});
11. Create a DataModel
@xeokit/sdk / data / DataModel / Class DataModel Contains a model's semantic data, as an entity-relationship graph.
const dataModel = data.createModel({
id: "demoModel"
});
12. Create a DataModelParamsLoader
@xeokit/sdk / data / DataModelParamsLoader / Class DataModelParamsLoader Reads DataModelParams into a DataModel.
const dataModelParamsLoader = new xeokit.data.DataModelParamsLoader();
13. Create an XGFLoader
@xeokit/sdk / xgf / XGFLoader / Class XGFLoader Loads an XGF file into a SceneModel and/or a DataModel.
const xgfLoader = new xeokit.xgf.XGFLoader();
14. Ignore the DemoHelper—used only to signal example completion
const demoHelper = new DemoHelper({});
demoHelper.init()
.then(() => {
15. Fetch the IFC file containing the source model
fetch("../../models/IfcOpenHouse4/ifc/model.ifc").then(response => {
response
.arrayBuffer()
.then(fileData => {
16. Convert the IFC file into XGF (geometry) and DataModelParams (semantics) using the ModelConverter
modelConverter.convert({
pipeline: "ifc2xgf",
inputs: {
"ifc": {
fileData
}
}
}).then(result => {
17. Load the XGF geometry into the SceneModel
xgfLoader.load({
fileData: result.outputs["xgf"].fileData,
sceneModel
}).then(() => {
18. Load the DataModelParams into the DataModel
dataModelParamsLoader.load({
fileData: result.outputs["datamodel"].fileData,
dataModel
}).then(() => {
19. Build the SceneModel and DataModel, to finalize the model structure. The Scene and SceneModel will then contain a SceneObject
@xeokit/sdk / scene / SceneObject / Class SceneObject An object within a SceneModel. @xeokit/sdk / data / DataObject / Class DataObject An object within a DataModel. @xeokit/sdk / viewer / ViewObject / Class ViewObject An object within a View.
dataModel.build();
sceneModel.build();
demoHelper.finished();
}).catch(message => {
console.error(`Error loading DataModel: ${message}`);
});
}).catch(message => {
console.error(`Error loading XGF: ${message}`);
});
}).catch(message => {
console.error(`Error converting IFC to XGF+DataModel: ${message}`);
});
});
});
});