Creating a Cube
This example demonstrates how to use the xeokit SDK to create and display a 3D box in the browser.
Click on the preview below to run the example. Scroll down to learn how it's made.
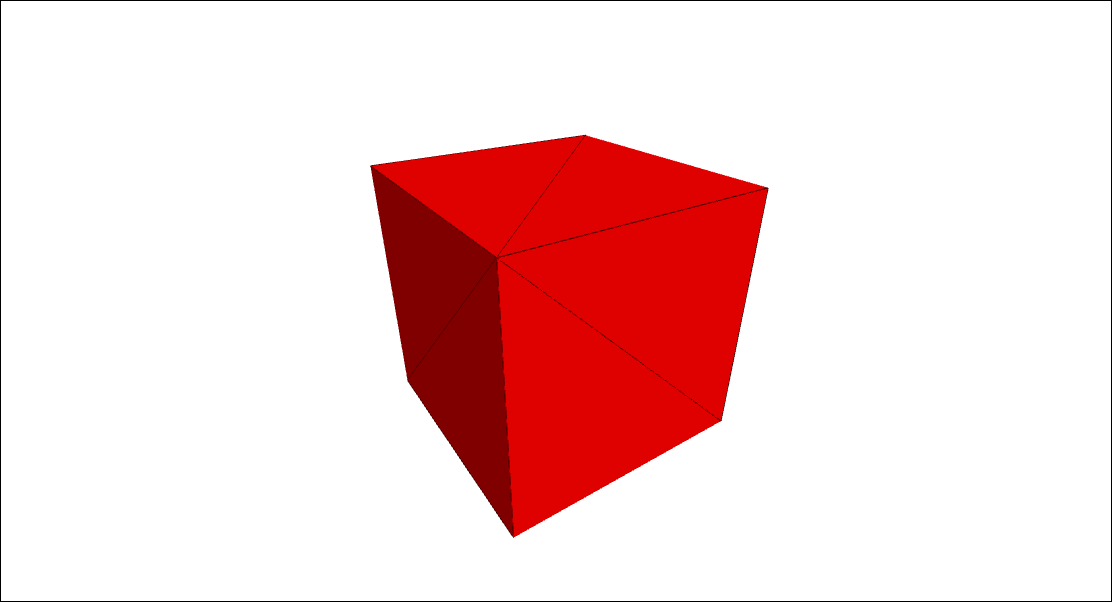
Creating a Cube
HTML
Listed below is the HTML for this example.
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Creating a Cube</title>
<style>
body {
background-color: white;
overflow: hidden;
margin: 0;
user-select: none;
}
#demoCanvas {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
position: absolute;
background: white;
border: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="demoCanvas"></canvas>
</body>
<script type="module" src="./index.js"></script>
</html>
JavaScript
Listed below is the JavaScript for this example, which we'll break down into steps.
1. Import the SDK from a bundle built for these examples
import * as xeokit from "../../js/xeokit-demo-bundle.js";
import {DemoHelper} from "../../js/DemoHelper.js";
2. Create a Scene
@xeokit/sdk / scene / Scene / Class Scene Container of model geometry and materials.
const scene = new xeokit.scene.Scene();
3. Create a WebGLRenderer
@xeokit/sdk / webglrenderer / WebGLRenderer / Class WebGLRenderer WebGL rendering strategy for a Viewer.
const renderer = new xeokit.webglrenderer.WebGLRenderer({});
4. Create a Viewer
@xeokit/sdk / viewer / Viewer / Class Viewer 3D model viewer.
const viewer = new xeokit.viewer.Viewer({
id: "demoViewer",
scene,
renderer
});
5. Ignore the DemoHelper
const demoHelper = new DemoHelper({
viewer
});
demoHelper.init().then(() => {
6. Create a single View
@xeokit/sdk / viewer / View / Class View An independent view within a Viewer, with its own canvas, Camera and object visual states.
const view = viewer.createView({
id: "demoView",
elementId: "demoCanvas"
});
7. Position the View's Camera
@xeokit/sdk / viewer / Camera / Class Camera Controls the viewpoint and projection for a View.
view.camera.eye = [2, 3, 2];
view.camera.look = [0, 0, 0];
view.camera.up = [0, 0, 1];
8. Add a CameraControl
@xeokit/sdk / cameracontrol / CameraControl / Class CameraControl Mouse and touch controller for a Viewer's Camera.
new xeokit.cameracontrol.CameraControl(view);
9. Within the Scene, create a SceneModel
@xeokit/sdk / scene / SceneModel / Class SceneModel Contains a model's geometry and materials.
const sceneModel = scene.createModel({
id: "demoModel"
});
10. Create a SceneGeometry
@xeokit/sdk / scene / SceneGeometry / Class SceneGeometry A geometry in a SceneModel.
sceneModel.createGeometry({
id: "boxGeometry",
primitive: xeokit.constants.TrianglesPrimitive,
11. Define the SceneGeometry vertices - eight for our box, each one spanning three array elements for X,Y and Z
positions: [
1.0, 1.0, 1.0, // v0-v1-v2-v3 front
-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
-1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0, // v0-v3-v4-v1 right
1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0, // v0-v1-v6-v1 top
1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
-1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
-1.0, 1.0, 1.0, // v1-v6-v7-v2 left
-1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
-1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
-1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
-1.0, -1.0, -1.0, // v7-v4-v3-v2 bottom
1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
-1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
1.0, -1.0, -1.0, // v4-v7-v6-v1 back
-1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
-1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
1.0, 1.0, -1.0
],
12. Define the SceneGeometry indices - these organise the positions coordinates into geometric primitives in accordance with the TrianglesPrimitive
@xeokit/sdk / constants / TrianglesPrimitive / Variable TrianglesPrimitive Non-closed triangle mesh primitive type.
indices: [
0, 1, 2, // Front
0, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6, // Right
4, 6, 7,
8, 9, 10, // Top
8, 10, 11,
12, 13, 14, // Left
12, 14, 15,
16, 17, 18, // Bottom
16, 18, 19,
20, 21, 22,// Back
20, 22, 23
]
});
13. Create a red SceneMesh
@xeokit/sdk / scene / SceneMesh / Class SceneMesh A mesh in a SceneModel.
sceneModel.createMesh({
id: "boxMesh",
geometryId: "boxGeometry",
position: [0, 0, 0], // Default
scale: [1, 1, 1], // Default
rotation: [0, 0, 0], // Default
color: [1.0, 0.0, 0.0] // Default is [1,1,1]
});
14. Create a SceneObject
@xeokit/sdk / scene / SceneObject / Class SceneObject An object within a SceneModel.
sceneModel.createObject({
id: "boxObject",
meshIds: ["boxMesh"]
});
15. Build the SceneModel, causing the red box to appear in the View's canvas.
sceneModel.build().then(() => {
16. At this point, the View will contain a single ViewObject
@xeokit/sdk / viewer / ViewObject / Class ViewObject An object within a View.
view.objects["boxObject"].highlighted = true;
view.setObjectsHighlighted(view.highlightedObjectIds, false);
17. Ignore the DemoHelper
demoHelper.finished();
}).catch(reason => {
console.error(reason);
demoHelper.finished();
});
});